What is Java?
Java is a high-level, class-based, object-oriented programming language. It is designed to have as few implementation dependencies as possible, making it a versatile and platform-independent language. Java is widely used for building enterprise-level applications, mobile apps, and web applications.
Definition:
- Java is a high-level, object-oriented programming language developed by Sun Microsystems (now owned by Oracle).
- Write Once, Run Anywhere (WORA) capability.
Uses:
- Web development, mobile apps, enterprise software, embedded systems, etc.
History:
- Created by James Gosling in 1995.
Visual:
- Timeline of Java versions or a world map showing Java’s impact globally.
Features of Java (Platform Independence, OOPs, Security, etc.)
- Platform Independence: Write Once and run Anywhere using JVM.
- Object-Oriented Programming (OOP): Supports encapsulation, inheritance, polymorphism, and abstraction.
- Security: Includes a security manager and bytecode verification.
- Robust: Exception handling and memory management.
- Other Features:
- High performance
- Multithreaded
- Dynamic
- Visual: Icons representing each feature.
Java Architecture
- JVM (Java Virtual Machine): Executes Java bytecode.
- JRE (Java Runtime Environment): Provides libraries and JVM for running Java programs.
- JDK (Java Development Kit): Includes JRE, compiler, and tools.
- Diagram: Java architecture flowchart.
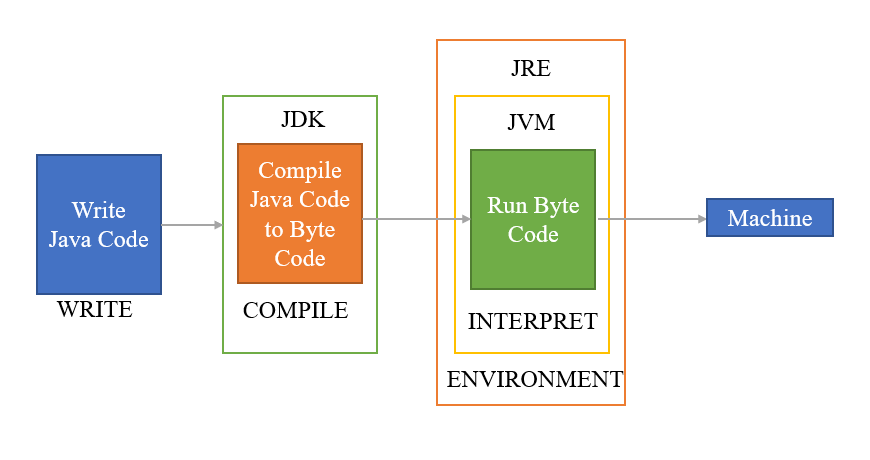
Java Development Kit (JDK), Java Runtime Environment (JRE), Java Virtual Machine (JVM)
- Java Development Kit (JDK): A software development kit to develop Java applications.
- Java Runtime Environment (JRE): Provides libraries and environment to run Java programs.
- Java Virtual Machine (JVM): An engine that executes Java bytecode.
* JDK includes JRE and development tools.
* JRE includes JVM and runtime libraries.
* JVM ensures platform independence.
Setting up the Java environment: Installing JDK and IDE (e.g., Eclipse/IntelliJ/NetBeans)
- Installing JDK:
1. Download the JDK from Oracle's official website.
2. Follow the installation steps and configure the PATH environment variable.
- Installing an IDE:
1. Choose an IDE like Eclipse, IntelliJ IDEA, or NetBeans.
2. Download and install the IDE.
3. Configure the IDE with the installed JDK for seamless development.
- Steps:
- Download JDK from the Oracle website.
- Install JDK and set the PATH environment variable.
- Install an IDE (Eclipse/IntelliJ IDEA/NetBeans).
- Demo:
- Show screenshots of JDK installation.
- Explain IDE setup briefly.
- Visual: Screenshots or a short flowchart.
Summary
- Recap key points:
- Java is platform-independent and secure.
- JDK, JRE, JVM are critical components.
- Setting up and writing simple Java programs is straightforward.
- Encourage further exploration:
- Practice more programs.
- Explore advanced features like multithreading, collections, etc.


No Comments