Network topologies refer to the physical or logical layout of devices and connections in a computer network. Different network topologies determine how data is transmitted, how devices are interconnected, and how network resources are shared. Here's a brief overview of some common network topologies:
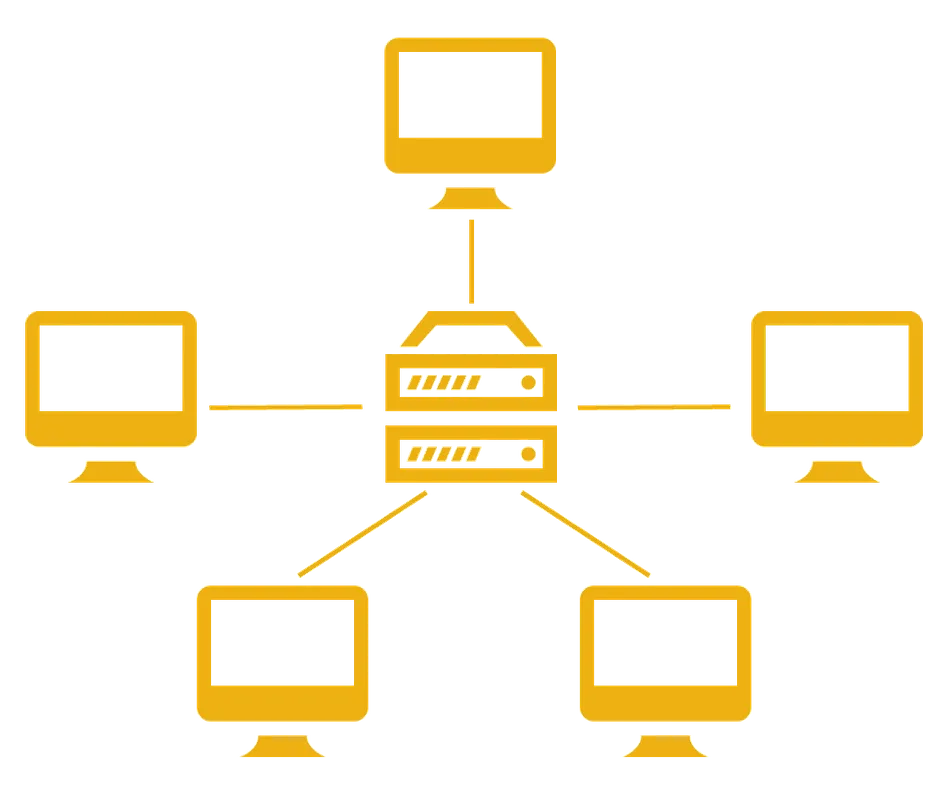
Star Topology:
- In a star topology, all devices (e.g., computers, printers) are connected to a central hub or switch.
- The central hub acts as a repeater and manages data traffic.
- If one device fails, it does not affect the rest of the network.
- It's commonly used in Ethernet LANs.
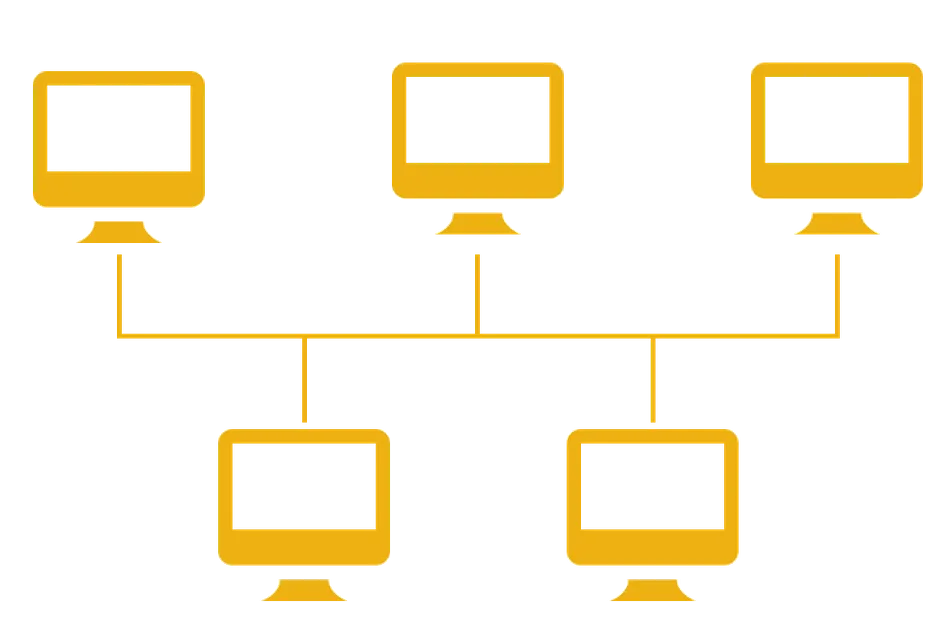
Bus Topology:
- In a bus topology, all devices are connected to a single central cable (the bus).
- Data travels along the cable, and each device on the network checks for data with its address.
- It's simple but can be prone to disruptions if the main cable is damaged.
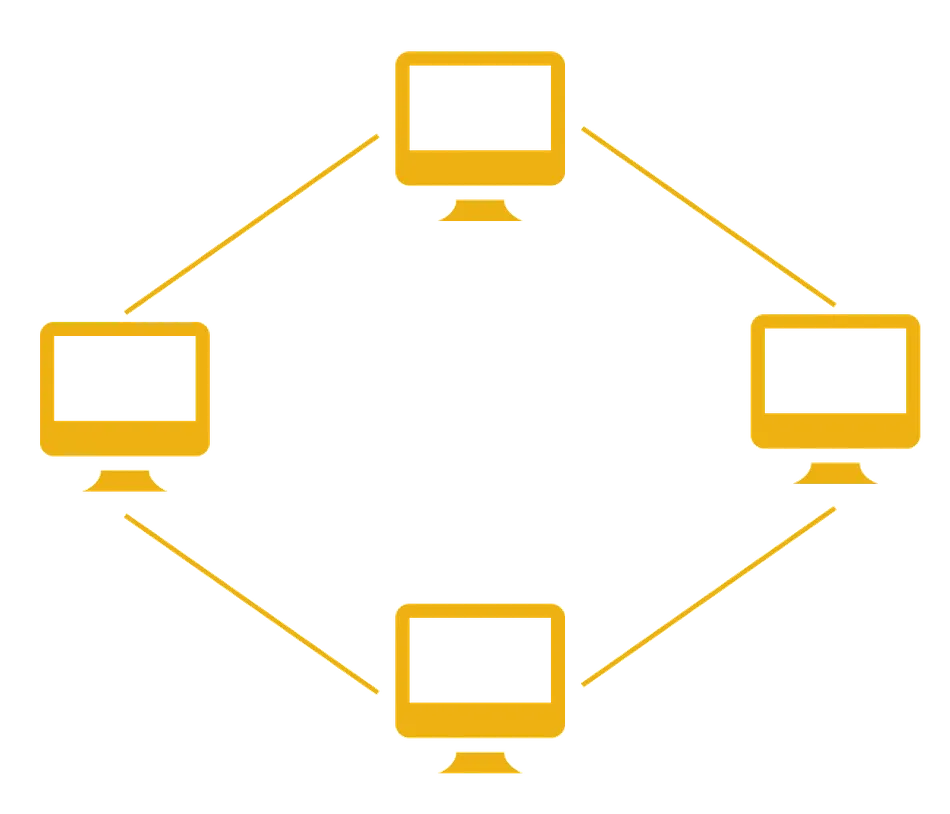
Ring Topology:
- In a ring topology, devices are connected in a closed loop.
- Data circulates in one direction, passing through each device until it reaches its destination.
- It's reliable, but a failure in one device can disrupt the entire network.
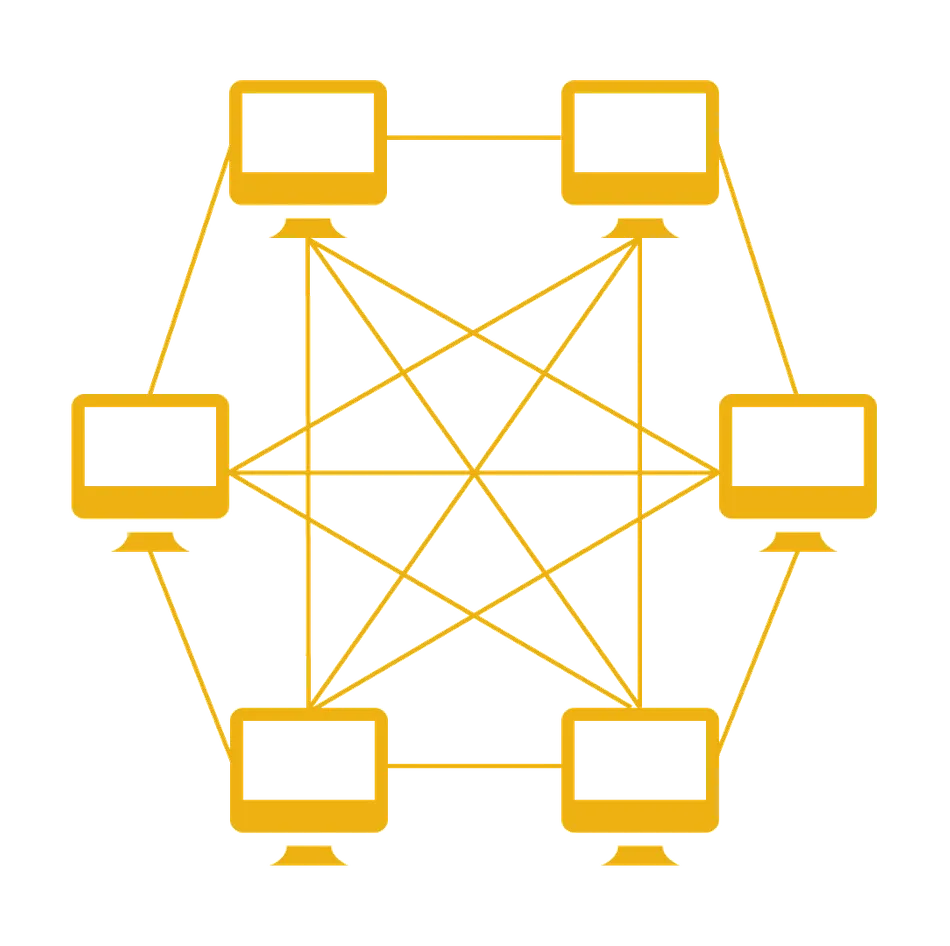
Mesh Topology:
- In a mesh topology, every device is connected to every other device.
- This provides redundancy and high reliability, but it can be expensive and complex to set up.
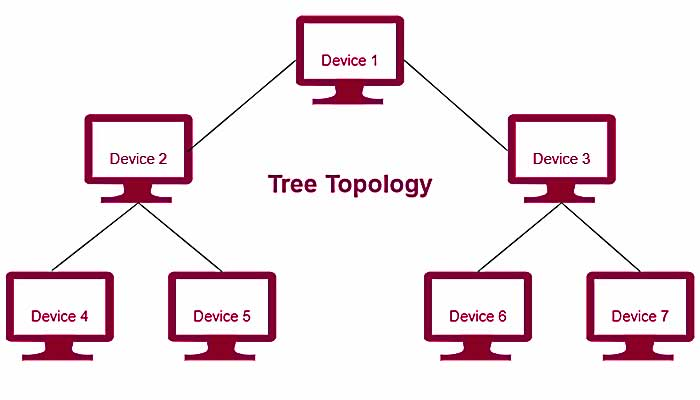
Tree (Hierarchical) Topology:
- A tree topology combines characteristics of a star and bus topology.
- It has a root node (main hub/switch) with branches and sub-branches.
- This is commonly seen in wide-area networks (WANs).
Hybrid Topology:
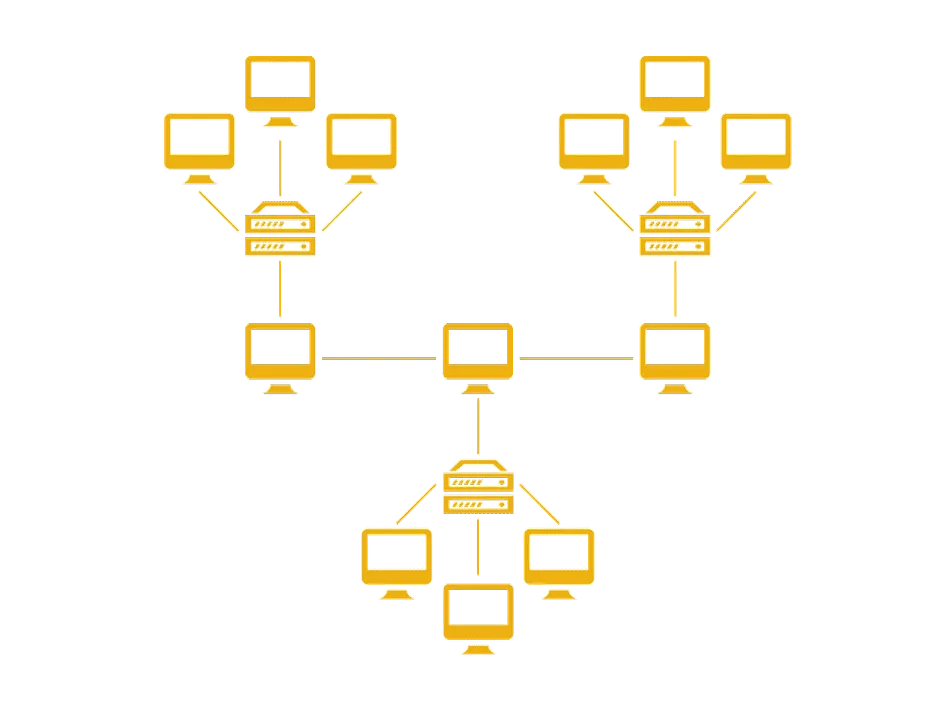
- A hybrid topology is a combination of two or more of the above topologies.
- This is used to take advantage of the strengths of different topologies and to meet specific network requirements.
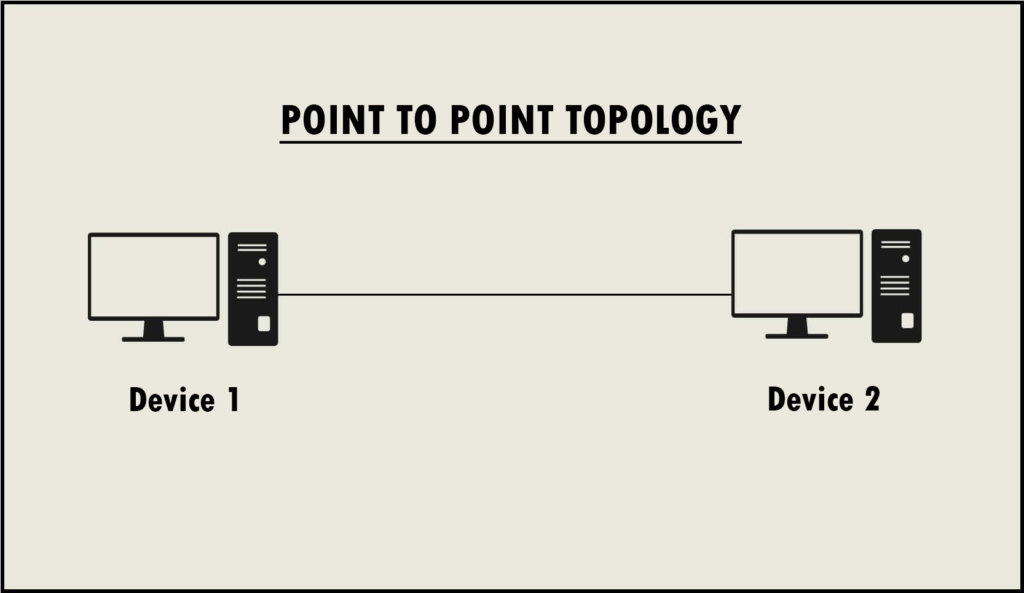
Point-to-Point Topology:
- In a point-to-point topology, two devices are directly connected.
- This is often used in telecommunications and wide-area network connections.
Wireless Mesh Topology:
- In a wireless mesh topology, devices are connected through wireless links.
- Every device can relay data for the network.
- It's commonly used in wireless networks and the Internet of Things (IoT).
Each of these network topologies has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of which one to use depends on factors like the size of the network, cost considerations, reliability requirements, and the specific needs of the network's users.


No Comments